Bartonella results in a disease called Bartonellosis
Bartonella are bacteria that live primarily inside the lining of the blood vessels. They can infect humans, mammals and a wide range of wild animals. The disease that results is called bartonellosis.
Bartonella henselae causes an important emerging infection that was first reported in 1990. It is mainly carried by cats and causes cat-scratch disease, endocarditis, and several other serious diseases in humans.
Transmission Of The Bartonella Bacteria
The bacteria is known to be carried by fleas, body lice and ticks, and there’s high suspicion that ticks transmit it to humans. People with tick bites and no known exposure to cats have acquired the disease. People who recall being bitten by ticks have been co-infected with the Lyme spirochete and bartonella. Scientists have recently established that ticks can transmit the bacteria to mice. More research needs to be done to establish the role of ticks in spreading the disease. In addition, a recent study suggests that the bacteria may be passed from mother to unborn child (perinatal transmission).
Several Species Of Bartonella
Scientists have identified several species of bartonella. Sand flies in the Andes Mountains in Peru, Colombia, and Ecuador carry one type. Human body lice worldwide carry another. European sheep ticks carry the bacteria and scientists have detected five different Bartonella strains in 19.2% of Ixodes pacificus ticks collected in California.
Bartonellosis Symptoms
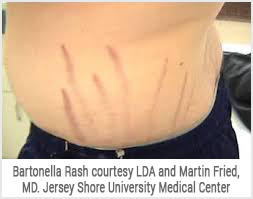
Early signs of bartonellosis include fever, fatigue, headache, poor appetite, and an unusual streaked rash that resembles “stretch marks” from pregnancy. Swollen glands are typical, especially around the head, neck and arms. Patients with bartonelliosis report more neurological symptoms and are more likely to have visited a neurologist than members of the general population. Some common symptoms include blurred vision, numbness in the extremities, memory loss, balance problems, headaches, ataxia (unsteady gait), and tremors. Bartonellosis also sometimes triggers psychiatric manifestations.
Bartonellosis Diagnosis and Treatment
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and tissue biopsy can be used. However they are also insensitive, as are standard blood tests. Dr. Ed Breitschwerdt, a professor of Veterinary Science at North Carolina State University who has studied bartonellosis extensively, notes that tests for the bacteria may be negative one time and positive another.
Fluoroquinolones and doxycycline are sometimes successful in treating bartonellosis. However, some doctors report the need to use several antibiotics in combination.
Learn more about Bartonellosis
CDC reports that they have identified six strains of Bartonella in patients with chronic symptoms.
FOCUS: CDC identifies new species of Bartonella in humans
CDC researchers report that they have identified six strains of the bacteria in patients with chronic subjective symptoms and a history of tick bites.
Bartonelleosis should be included in the differential diagnosis for patients exposed to tick bites.
HARD SCIENCE ON LYME: Research Finds Bartonella Transmission from Tick to Host
This research is very important to patients with Lyme disease because it confirms that the transmission of the bacteria from ticks may produce Bartonelleosis.

















