Federal funding for Lyme and other TBD nearly triples in 3 years

Bonnie Crater, of the Center for Lyme Action, provides the following update on federal Lyme disease funding.
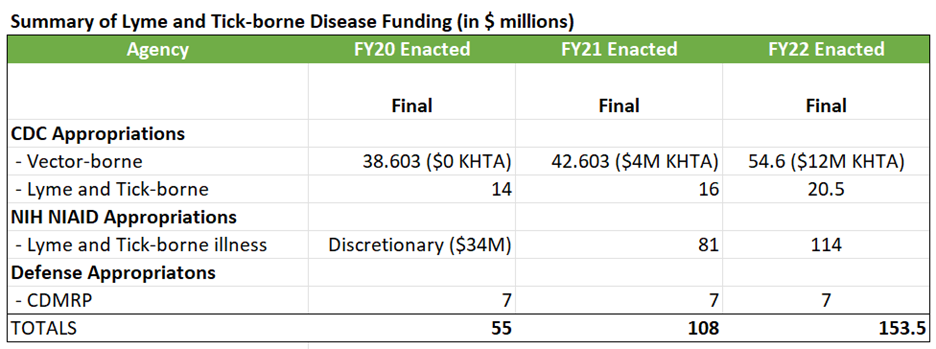
Nearly three times the funding in three years
Our work together in the last few years has been very effective. When we started on this journey Lyme and Tick-borne disease was funded at $55 million in FY20.
Three years later Congress has appropriated nearly 3 times that much in FY22: $153.5M.
We are still at the beginning of our journey, but we are making great progress.
CONSOLIDATED APPROPRIATIONS ACT, 2022
Division H – Departments of Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act, 2022
https://docs.house.gov/billsthisweek/20220307/BILLS-117RCP35-JES-DIVISION-H_Part1.pdf
CDC
EMERGING AND ZOONOTIC INFECTIOUS DISEASES pp.22-25
Vector-Borne Diseases …………………………………. . 54,603,000 [FY21 & FY22 PBR $42,603,000/ KHTA $16M]
Lyme Disease………………………………………………. 20,500,000 [FY21 & FY22PBR $16,000,000]
Lyme Disease and Related Tick-Borne Illnesses.-The agreement provides an increase in recognition of the importance of the prevention and control of Lyme disease and related tick-borne diseases, and encourages CDC to support surveillance and prevention of Lyme disease and other high consequence tick-borne diseases in endemic areas as well as areas not yet considered endemic.
The agreement includes funding for CDC’s vector-borne diseases program to expand the programs authorized under the Kay Hagan Tick Act (P.L. 116-94) to promote a public health approach to combat rising cases of tick-borne diseases, including activities directed in House Report 117-96.
CDC is directed to develop and implement methods to improve surveillance to more accurately report the disease burden, including through the development of real time data for reporting Lyme disease and other tick-borne diseases, as well as a process for estimating the prevalence of Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome.
CDC is directed to direct funding to improve early diagnosis of Lyme and related tick-borne diseases to prevent the development of late stage disease and more serious and long-term disability.
CDC is encouraged to coordinate with the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the National Institute of Mental Health, and the National Institute of 24 Neurological Disorders and Stroke on publishing reports that assess diagnostic advancements, methods for prevention, the state of treatment, and links between tick-borne disease and psychiatric illnesses.
CDC is urged, in coordination with NIH, to include in their surveillance the long-term effects on patients suffering from post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome, or “chronic Lyme disease.”
Additionally, given the impact of Lyme disease and the status of ongoing clinical trials, the agreement requests a report within 180 days of enactment of this Act on CDC’s research to date and recommendations on actions needed to facilitate a successful Lyme disease vaccine rollout that will build confidence and encourage uptake should a vaccine be approved by the FDA.
Kay Hagan Tick Act. CDC vector-borne diseases programs increased by $12 M ($54.6 M total) and Lyme disease increased by $4.5 M ($20.5 M total) to support implementation of the Kay Hagan Tick Act. Source: Senate Appropriations Committee.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF ALLERGY AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES (NIAID) pp55-56
Lyme Disease and Other Tick-Borne Diseases.-The agreement includes a $18,000,000 increase for Lyme disease and other tick-borne illnesses research.
The agreement encourages NIAID to use these funds to prioritize the support of meritorious research that informs a better understanding of Lyme disease pathogenesis and encourages the development of improved diagnostics and vaccines.
The agreement directs NIH to leverage this understanding to develop 55 new tools that can more effectively prevent, diagnose, and treat Lyme disease, including long-term effects, and other tick-borne diseases.
The agreement encourages the promotion and development of potential vaccine candidates for Lyme disease and other tick-borne diseases.
The agreement directs NIH to conduct research to better understand modes of transmission for Lyme and other tick-borne diseases, including vertical transmission.
The agreement urges NIH to incentivize new investigators to enter the field of Lyme disease and other tick-borne disease research.
The agreement directs NIH to coordinate with CDC on publishing reports that assess diagnostic advancements, methods for prevention, the state of treatment, and links between tick-borne disease and psychiatric illnesses.
NIH Lyme and Tick-borne disease research. Research funding increased by $18M, for a total of $114M. Source: Senate Appropriations Committee.
ADVANCED RESEARCH PROJECTS AGENCY FOR HEALTH
The agreement includes $1,000,000,000 and bill language to establish the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health within the Office of the Secretary.
DIVISION C – DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE APPROPRIATIONS ACT, 2022
Defense Health Program P.114
https://docs.house.gov/billsthisweek/20220307/BILLS-117RCP35-JES-DIVISION-C_Part2.pdf
Peer-reviewed tick-borne disease research……………………$7,000,000




















We invite you to comment on our Facebook page.
Visit LymeDisease.org Facebook Page