B artonella bacteria are increasingly recognized as an emerging infectious disease threat. A new study by North Carolina State University researchers has found additional instances of Bartonella infection in humans who exhibited neuropsychiatric symptoms, a subset of whom also had skin lesions.
This research adds to the body of evidence that suggests that not only can Bartonella infection mimic a spectrum of chronic illnesses—including mental illness—but also that dermatological symptoms may accompany infection.
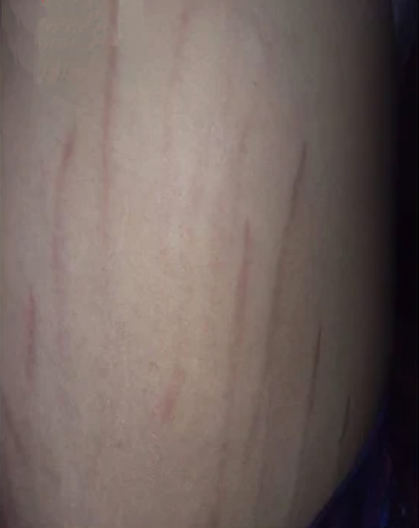
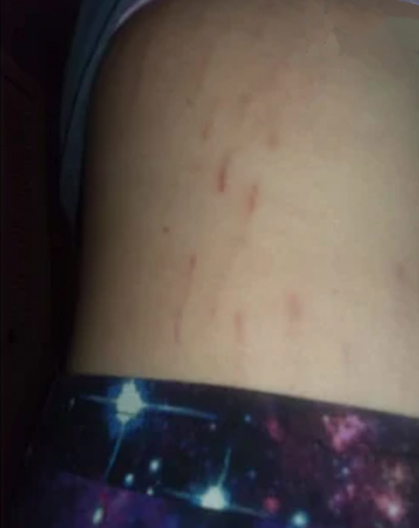
Bartonella-Associated Cutaneous Lesions. Twenty-one-year-old female veterinary assistant from Louisiana, with neuropsychiatric symptoms of 2 years’ duration. Serpiginous, vertical red lesions on the left abdomen (a) and the right upper side of the abdomen (b). Positive for Bartonella infection by ddPCR from direct EDTA blood sample and enrichment blood culture (Bartonella henselae and Bartonella koehlerae IFA titers of 1:256 and 1:64, respectively). Photo provided by the study participant.
Bartonella henselae is a bacterium historically associated with cat-scratch disease, which until recently was thought to be a short-lived (or self-limiting) infection. There are at least thirty different known Bartonella species, of which thirteen have been found to infect humans…..Join or login below to continue reading.